In the intricate tapestry of human emotions, anxiety is a thread that everyone experiences at some point in life. It's that uneasy feeling before a big presentation or the jittery excitement before a first date. Yet, when anxiety transcends the normal ebb and flow of emotions, individuals may turn to substances like drugs or alcohol in an attempt to find solace.
Understanding Anxiety
Everyday anxiety, often referred to as non-clinical anxiety, is a common human experience. It's the feeling of unease, worry, or fear that arises in response to life's challenges. Symptoms may manifest as a racing heart, sweaty palms, restlessness, or a nagging sense of apprehension. This type of anxiety is a natural part of the human experience, but when it starts to interfere significantly with daily life, it can become problematic.
However, when this gentle worry becomes overwhelming, turning into a constant downpour, it can become a significant challenge. It's no longer just occasional stress but a continuous storm that threatens to overpower and affect mental well-being. Beyond the physical signs, everyday anxiety involves mental and emotional aspects. Persistent thoughts about the future, a sense of impending doom, and difficulty sleeping can become prevalent. Relationships may also feel the strain of this emotional turbulence.
It's important to note that everyday anxiety isn't the same for everyone; it comes in various forms, adapting to individual experiences. Social anxiety, where one fears judgment in social situations, might lead to sweaty palms and a racing heart. Performance anxiety can cast a shadow on achievements, turning them into sources of potential stress.
The Role of Substance Use in Everyday Anxiety
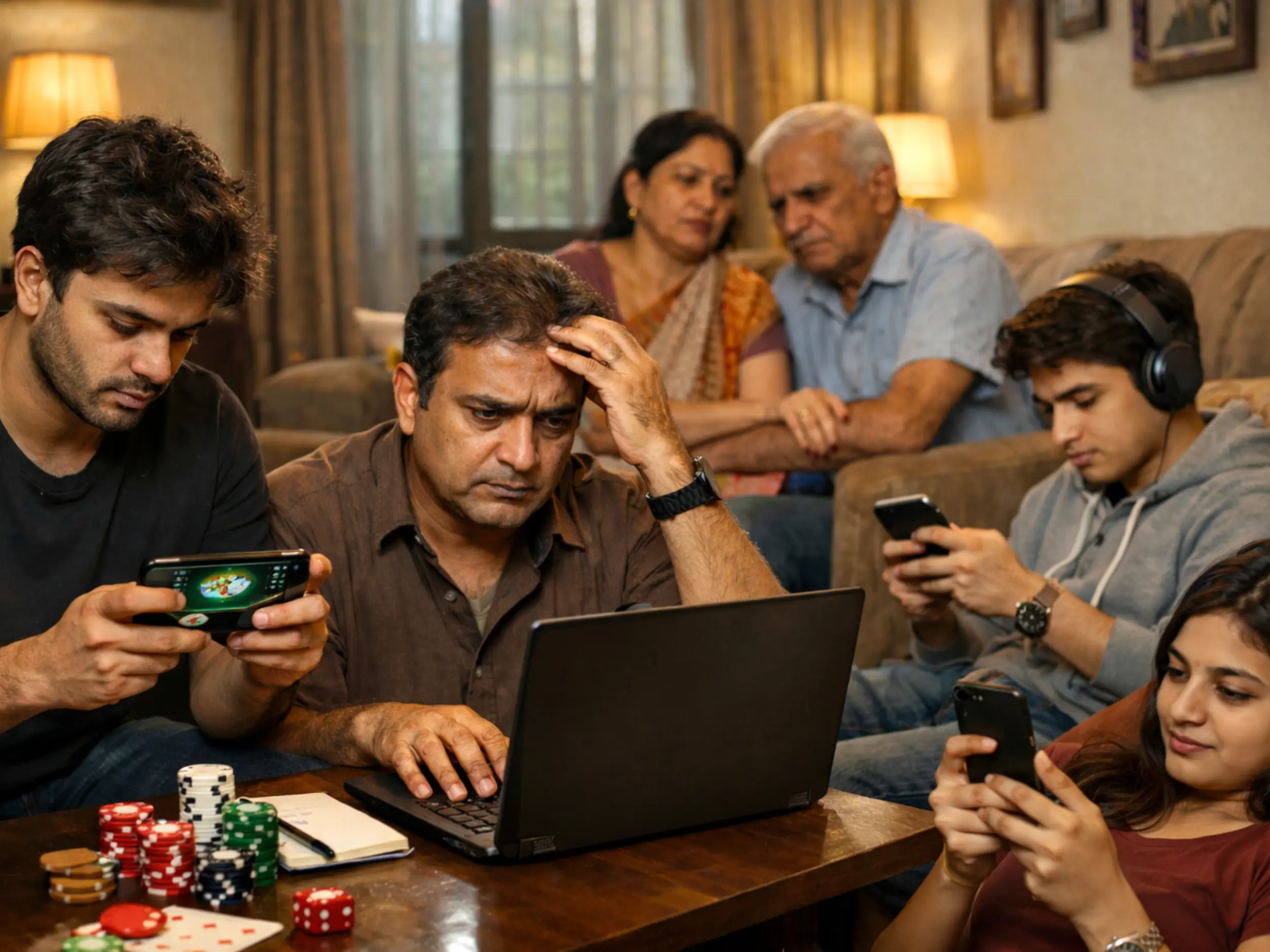
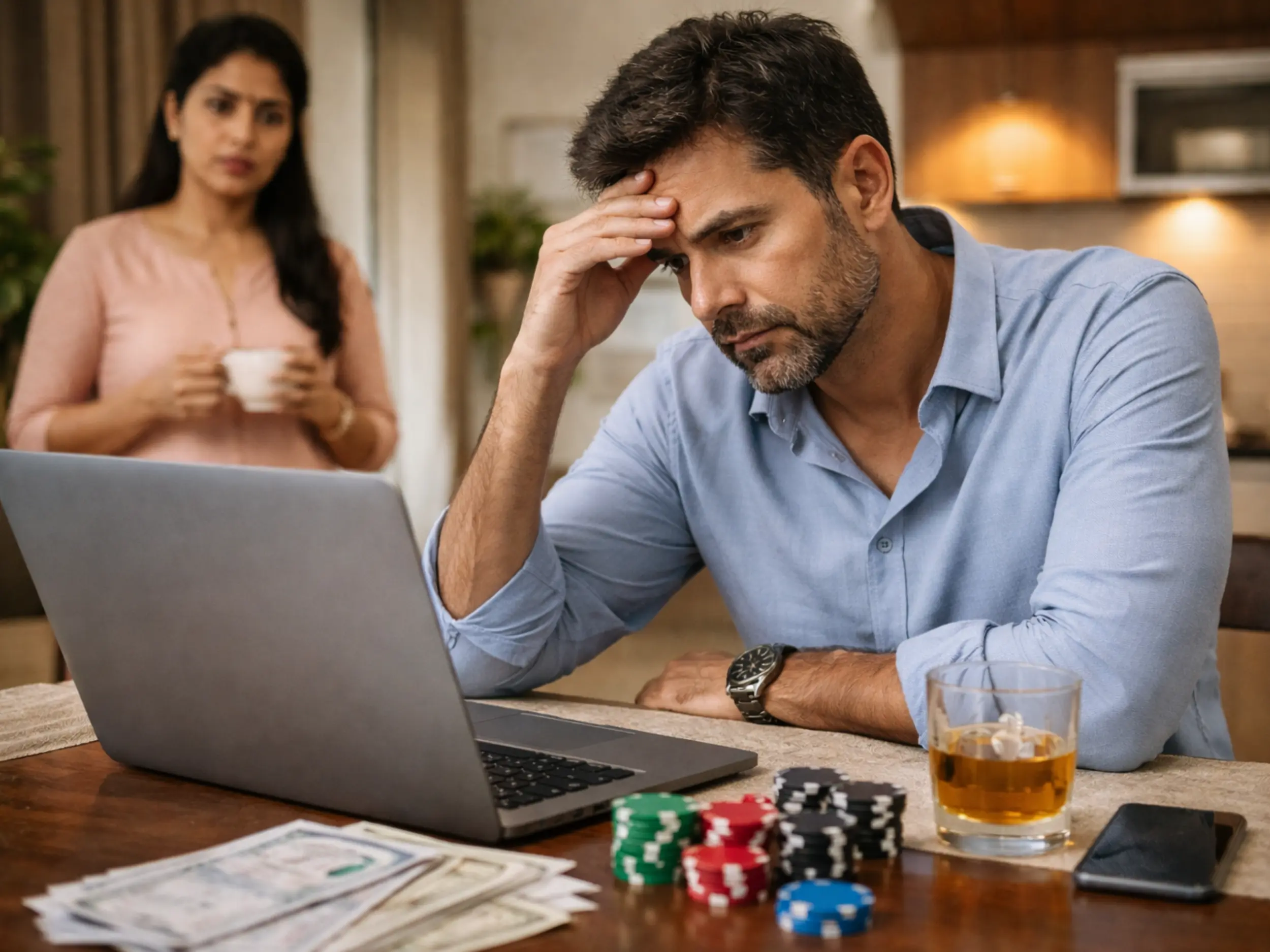
Anxiety is a natural response to stress, preparing the body for the 'fight or flight' response. However, when this response becomes chronic and disproportionate to the stressor's magnitude, it transforms into a mental health disorder. Common symptoms of anxiety include persistent worry, restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, muscle tension, and sleep disturbances. In the quest for relief from the strains of everyday anxiety, some individuals turn to substances, hoping for a temporary escape. A couple of drinks to take the edge off or reaching for a joint to relax can seem like quick fixes. However, this coping mechanism can inadvertently deepen the connection between anxiety and substance use, leading to a cycle that's challenging to break.
Correlation between Everyday Anxiety and Substance Use Disorder Research by Johnson (2021) sheds light on the interplay between everyday anxiety and substance use. The study found that individuals with higher levels of non-clinical anxiety were more likely to engage in problematic substance use. This highlights the bidirectional nature of the relationship, where anxiety can drive substance use, and substance use can, in turn, exacerbate anxiety. The study also emphasized the importance of early intervention. Identifying non-clinical anxiety and addressing it before it escalates can be a crucial step in preventing the development of a more severe substance use disorder. This underscores the need for accessible and community-based mental health resources that can provide support and education on managing everyday anxiety.
Effective Strategies for Managing Everyday Anxiety and Substance Use Disorder
1. Psychotherapy:
Engaging in talk therapy, such as counseling or support groups, can provide a safe space to explore and address the root causes of everyday anxiety. Simple conversations can be powerful tools for developing coping mechanisms and breaking the reliance on substances.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT, a widely used form of psychotherapy, focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns. By challenging irrational beliefs and replacing them with healthier alternatives, individuals can develop more effective coping strategies.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): DBT combines cognitive-behavioral techniques with mindfulness. It helps individuals regulate emotions, improve interpersonal effectiveness, and build distress tolerance skills.
2. Rehabilitation Programs:
For those caught in the web of substance use, rehabilitation programs offer structured support. These programs, as outlined by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), provide a combination of medical and therapeutic interventions, aiding individuals in breaking the cycle of substance use and managing underlying anxiety.
- Individualized Treatment Plans: Effective rehabilitation programs tailor interventions to individual needs, addressing both substance use and underlying anxiety. This might include detoxification, counseling, and aftercare planning.
- Holistic Approaches: Some programs incorporate holistic therapies like art or music therapy, providing alternative avenues for self-expression and stress relief.
3. Physical Activities:
Regular physical activities, like walking, jogging, or dancing, can be effective in managing everyday anxiety. Exercise releases endorphins, the body's natural stress relievers, contributing to an improved mood and overall well-being.
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities like running or swimming, known as aerobic exercises, have been linked to reductions in anxiety symptoms. Aim for at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
- Mindful Movement Practices: Incorporating mindful movement practices like tai chi or qi;ng combines physical activity with relaxation techniques, promoting a sense of calm.
4. Yoga and Meditation:
Mindfulness practices, such as yoga and meditation, offer accessible techniques to alleviate everyday anxiety. These practices focus on the present moment, teaching individuals to manage their thoughts and emotions without turning to substances.
- Mindful Breathing: Simple breathing exercises, like diaphragmatic or deep belly breathing, can be done anywhere and are effective in calming the nervous system.
- Guided Imagery: Visualization exercises, guided by calming imagery, can help redirect the mind away from anxious thoughts.
5. Healthy Lifestyle Changes:
Implementing positive lifestyle changes can have a profound impact on anxiety and substance use. This includes adopting a balanced diet, ensuring adequate sleep, and reducing stimulants like caffeine and nicotine.
- Nutrition and Mental Health: Research suggests a link between diet and mental health. Nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, support brain function and may contribute to better emotional well-being.
- Quality Sleep: Establishing a consistent sleep routine and creating a sleep-friendly environment can enhance the quality of sleep, positively impacting anxiety levels.
6. Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR):
MBSR programs, incorporating mindfulness meditation and yoga, have shown promise in reducing anxiety and preventing relapse in individuals with substance use disorders (Bowen et al., 2014). These programs emphasize present-moment awareness and non-judgmental acceptance.
- Body Scan Meditation: This technique involves directing focused attention to different parts of the body, promoting relaxation and awareness.
- Mindful Eating: Applying mindfulness to eating habits can enhance the enjoyment of food and help individuals become more attuned to hunger and fullness cues.
7. Peer Support Groups:
Joining peer support groups, such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or SMART Recovery, provides individuals with a sense of community and understanding. Sharing experiences and coping strategies with others facing similar challenges can be empowering.
- Online Support Communities: In the digital age, online platforms offer accessible support. Forums and virtual meetings provide avenues for connecting with others, especially in times when in-person gatherings might be challenging.
8. Role and support of Family:
The support of family is instrumental in the recovery process. Understanding and empathy from loved ones create a supportive environment, aiding in the individual's journey to overcome both anxiety and substance use disorder. Simple gestures like active listening, understanding, and encouragement create a nurturing environment that can empower individuals to tackle both everyday anxiety and substance use.
- Education and Communication: Family education becomes a beacon, illuminating the path to understanding. Open conversations dismantle the walls of stigma, creating a space where individuals can seek help without fear of judgment.
- Establishing Healthy Boundaries: Healthy boundaries become the notes of harmony, fostering an environment where support and encouragement coexist without enabling destructive behaviors.
The family's role in supporting individuals with anxiety and substance use disorder cannot be overstated. A study conducted by Brown (2022) found that family involvement significantly contributed to positive treatment outcomes. The study emphasized the importance of family education, communication, and the establishment of healthy boundaries to create a supportive environment for recovery.
Moreover, the study highlighted the need for destigmatizing mental health issues within families. Open conversations about anxiety and substance use can foster understanding and encourage individuals to seek help without fear of judgment. This family-centric approach aligns with the broader shift in mental health discussions, recognizing the influence of social support in the recovery journey.
Conclusion
The connection between anxiety and substance use disorder is a nuanced interplay that impacts many. By understanding the relationship between these two aspects of mental health, individuals can embark on a journey of recovery. Practical strategies, including psychotherapy, rehabilitation, physical activities, yoga, meditation, healthy lifestyle changes, mindfulness-based stress reduction, and family support, offer a roadmap for breaking free from the cycle. It's a journey that emphasizes simplicity, understanding, and the innate resilience that lies within every individual. As we navigate the landscape of mental health, it becomes imperative to continue destigmatizing conversations around anxiety and substance use. Public awareness, accessible resources, and community support can pave the way for individuals to seek help, fostering a culture that prioritizes mental well-being.
Why choose Samarpan?
Samarpan is a specialized international Substance Use Disorder (De-Addiction) and Process Addiction rehab in Pune, India that accepts a maximum of 26 clients. We only accept clients on a voluntary basis and have a highly structured program that encompasses the most effective approaches to Substance Use Disorder and addiction. The facility is set in the rolling hills Mulshi, with clients having either individual or shared rooms, in a modern resort like facility, staffed by Internationally Accredited Professionals. Samarpan is fully licensed under The MSMHA and is also an accredited ;RSKI-CENAPS Centre of Excellence offering a program from 5 to 13 weeks.
If you or someone you care about is considering treatment for substance use disorder or process addictions, we can help. Contact us now on admissions@samarpan.in or phone/WhatsApp us on +91 81809 19090.
References:
- Johnson, K. J., … (2021). Exploring the Bidirectional Association Between Anxiety and Substance Use in a Population-Based Study. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.;v/pmc/articles/PMC8204243/
- Brown, A., … (2022). Family involvement in the treatment of anxiety and substance use disorders: A systematic review. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.;v/pmc/articles/PMC8861326/
- Bowen, S., … (2014). Mindfulness-Based Relapse Prevention for Substance Use Disorders: A Pilot Efficacy Trial. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.;v/pmc/articles/PMC4063334/