Mephedrone vs. MDMA: Understanding the Key Differences and Addiction Risks
There’s a particular kind of chaos that unfolds when drugs with glittery reputations become part of mainstream nightlife—like uninvited guests at a wedding who spike the punch, charm the guests, and then leave behind a mess no one talks about. MDMA and Mephedrone are two such party drugs—both adored, abused, misunderstood, and more dangerous than their neon-drenched reputations let on.
At a glance, they might look like cousins: both stimulants, both typically used in club and rave scenes, and both associated with euphoric highs, heightened sensory perception, and the kind of affection for strangers that only serotonin floods can cause. But beneath their effects lie very different chemical profiles, risks, and treatment needs.
Let’s dive into the differences between MDMA (also known as Molly or Ecstasy) and Mephedrone (often called Meow Meow), how they affect the brain, the warning signs of dependency, and the path toward healing if someone finds themselves caught in their grasp.
The Basics: What Are MDMA and Mephedrone?
MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine) is a synthetic drug that acts as both a stimulant and a hallucinogen. It increases the activity of three brain chemicals: dopamine, norepinephrine, and, most notably, serotonin. This rush of serotonin is what causes the flood of emotional closeness, love, and euphoria often associated with the drug.
MDMA has been widely researched, not just as a party drug but as a possible treatment for PTSD through MDMA therapy. While the therapeutic use is promising, recreational misuse often leads to MDMA addiction, dependency, and severe MDMA withdrawal symptoms like depression, fatigue, and anxiety once the high fades.
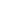
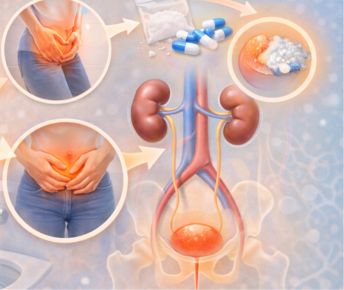
Mephedrone (4-methylmethcathinone), on the other hand, is a synthetic stimulant in the cathinone class—meaning it's chemically similar to compounds found in the khat plant. It gained popularity in the mid-2000s as a legal high and quickly earned notoriety for its intense euphoric and stimulant effects. It’s often snorted, swallowed, or even injected, with an onset that's rapid and effects that resemble a more aggressive mix of cocaine and MDMA.
While MDMA’s high has been described as warm and empathetic, Mephedrone tends to feel sharper, faster, more compulsive. It's the kind of drug that can leave someone binging for hours or even days—chasing a high that never quite returns to its original peak.
How They Work in the Brain
MDMA is famous for releasing serotonin, which in turn regulates mood, sleep, pain, and emotions. It also causes the release of dopamine (linked to pleasure and reward) and norepinephrine (which increases heart rate and energy). The intense emotional and sensory experiences occur because your brain is quite literally flooded with feel-;od chemicals.
But this flooding comes at a cost. When serotonin levels are depleted after MDMA use, users can experience the infamous "Tuesday blues"—a depressive crash that can trigger emotional dysregulation, hopelessness, or, in severe cases, suicidal ideation. For frequent users, this crash can spiral into full-blown MDMA addiction and the need for MDMA addiction treatment.
Mephedrone also releases serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine but is more aggressive in action. The onset is quicker, the craving stronger, and the comedown even harsher. Repeated use in one session is everyday, leading to binge behavior. Users report increased impulsivity, paranoia, and severe mood swings after use—making Mephedrone addiction particularly dangerous.
So yes, Mephedrone does release serotonin, but with less finesse and a more jarring effect on the nervous system. And no, methylphenidate is not the same as MDMA. Methylphenidate (commonly known as Ritalin) is a stimulant prescribed for ADHD, acting on dopamine and norepinephrine but not serotonin. The comparison is like calling a rainstorm and a flood the same thing—they're related but hit differently.
Addiction, Withdrawal, and Recovery
Addiction to either MDMA or Mephedrone often starts subtly. A festival here, a party there, a night where everything feels more manageable, warmer, more magical. But with frequent use, the brain’s natural reward system takes a hit. Suddenly, you’re not just doing Molly for fun—you’re doing it to feel normal.
Signs of MDMA or Mephedrone addiction can include:
- Obsessive thoughts about using
- Using despite negative consequences
- Increased tolerance
- Emotional crashes post-use
- Social withdrawal or irritability when sober
- Binge behavior or combining with other substances
MDMA withdrawal symptoms may include insomnia, fatigue, depression, anxiety, and memory issues.
Mephedrone withdrawal often includes severe cravings, tremors, paranoia, and deep emotional dysregulation.
While both substances pose serious risks, Mephedrone addiction treatment often requires a more aggressive and trauma-informed approach due to its high relapse potential and binge pattern.
MDMA addiction treatment may include psychotherapy, especially CBT and trauma-informed care, alongside medical monitoring.
Treatment should happen under the guidance of professionals at a substance abuse treatment center or a rehabilitation facility that understands the nuances of stimulant addiction. While detox is not always physically dangerous for these drugs (unlike alcohol or benzodiazepines), the psychological toll can be devastating.
Therapeutic Use vs Recreational Misuse
It’s worth noting that MDMA is being studied for therapeutic use, particularly in treating severe PTSD. However, this is not the same as recreational use. The substance is used in microdoses under strict supervision in a clinical setting, with trained therapists guiding the experience.
Using MDMA from an unknown source, with unknown additives, and in uncontrolled environments increases the risk of adverse outcomes—especially when people are unknowingly taking MDA, PMA, or bath salts misrepresented as Molly.
As for Mephedrone, there’s no established or recommended therapeutic use. Its quick addiction profile and high-risk binge patterns mean it is solely viewed as a harmful substance with no clinical benefit.
Which Is "Worse"?
That’s like asking, "What’s worse, drowning in a pool or the ocean?"
Mephedrone is arguably more dangerous because it’s more addictive, less predictable, and more commonly linked to erratic behavior, violence, and psychosis. The comedown is intense, and the cravings are almost immediate.
MDMA can feel gentler, especially in social settings, but the risks remain significant: long-term serotonin depletion, memory issues, emotional flattening, and, of course, the risk of MDMA dependency.
But neither is safe. Neither is "better". Both hijack the brain's reward circuitry, and both can lead to psychological dependency.
Recovery Options and Treatment Approaches
If you or someone you love is caught in the loop of Molly addiction, Ecstasy addiction, or Mephedrone dependency, know that help is available. Ecstasy addiction treatment often includes counseling, lifestyle restructuring, and trauma recovery work. Mephedrone addiction treatment, on the other hand, may require more intensive behavioral interventions and long-term psychological support. Regardless of the substance, a substance abuse treatment plan that includes medical professionals, emotional regulation techniques, and social support is key.
FAQs
What is better than MDMA?
Neither MDMA nor Mephedrone is “better.” While MDMA may have therapeutic potential under clinical supervision, recreational use of either substance carries serious risks.
What’s the difference between MDA and MDMA?
MDA is a related compound, often more hallucinogenic and longer lasting, but with higher neurotoxicity than MDMA.
Does Mephedrone release serotonin?
Yes, it releases serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, but its impact is harsher and more compulsive.
Is methylphenidate the same as MDMA?
No. Methylphenidate (Ritalin) is a stimulant used to treat ADHD. MDMA is a psychoactive party drug with hallucinogenic properties.
How can Samarpan help?
At Samarpan, we provide evidence-based treatment for individuals struggling with drug addiction, including dependencies on synthetic stimulants like Mephedrone and MDMA. Both substances, often used recreationally, carry high risks for developing addictive behaviors and experiencing severe substance withdrawal symptoms. These drugs can significantly impact mental health, leading to heightened anxiety symptoms, depression symptoms, and in some cases, triggering underlying personality disorders. As a dedicated drug recovery center, Samarpan offers tailored drug addiction therapy and de-addiction therapy to address the specific effects of stimulant abuse. Our approach includes medical detox to manage withdrawal relief symptoms, along with psychological support, counseling, and relapse prevention strategies. We also emphasise mental health awareness, ensuring that clients are educated about the long-term effects of drug use and the importance of emotional and psychological healing. Through integrative care that combines traditional therapies with health, nutrition and optional alcohol detoxification services, Samarpan helps clients rebuild their lives free from dependence.





















 Yes, many offer serene environments and solid therapeutic frameworks. However, quality varies, so it’s essential to research accreditation, staff credentials, and therapeutic depth.
Yes, many offer serene environments and solid therapeutic frameworks. However, quality varies, so it’s essential to research accreditation, staff credentials, and therapeutic depth.